Conditions of the Ball Screw
| Transfer orientation | (horizontal, vertical, etc.) |
|---|---|
| Transferred mass | m(kg) |
| Table guide method | (sliding, rolling) |
| Frictional coefficient of the guide surface | μ(-) |
| Guide surface resistance | f(N) |
| External load in the axial direction | F(N) |
| Desired service life time | Lh(h) |
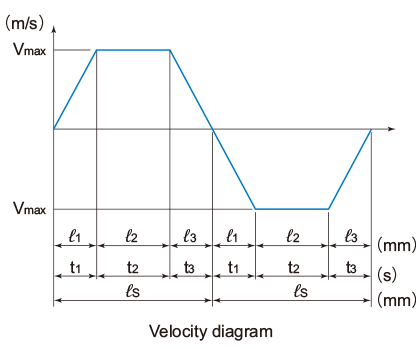
| Stroke length | ℓs(mm) |
| Operating speed | Vmax(m/s) |
| Acceleration time | t1(s) |
| Even speed time | t2(s) |
| Deceleration time | t3(s) |
| Acceleration |
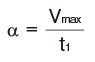
|
| Acceleration distance | ℓ1=Vmax×t1×1000/2(mm) |
| Even speed distance | ℓ2=Vmax×t2×1000(mm) |
| Deceleration distance | ℓ3=Vmax×t3×1000/2(mm) |
| Number of reciprocations per minute | n(min-1) |
| Positioning accuracy | (mm) |
| Positioning accuracy repeatability | (mm) |
| Backlash | (mm) |
| Minimum feed amount | s (mm/pulse) |
| Driving motor (AC servomotor, stepping motor, etc.) | |
| The rated rotation speed of the motor | NMO(min-1) |
| Inertial moment of the motor | JM(kg・m2) |
| Motor resolution | (pulse/rev) |
| Reduction ratio | A(-) |
Point of Selection
- Conditions of the Ball Screw
- Conditions of the Ball Screw
- Estimating the shaft length
- Selecting lead・Selecting a shaft diameter
- Method for Mounting the Ball Screw Shaft
- Permissible Axial Load
- Permissible Rotational Speed
- Selecting a Nut
- Calculating the permissible axial load
- Studying the Service Life
- Studying the Rigidity
- Studying the Positioning Accuracy
- Studying the Rotational Torque
- Studying the Driving Motor