Jul 19, 2023
Products
Seismic Isolation: An Inside Look at the Development, Structure, and Applications
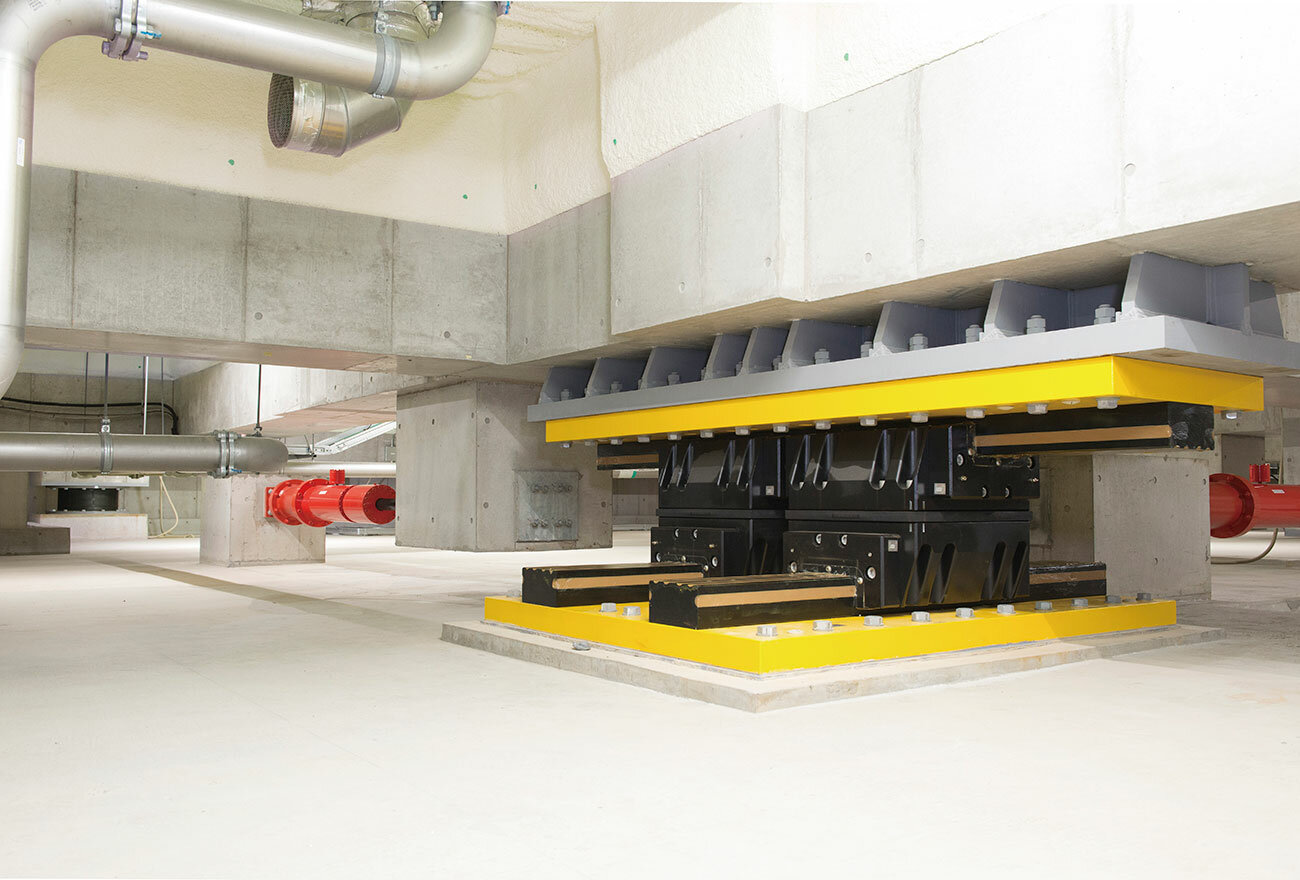

Seismic isolation structures work to shield buildings from seismic energy coming through the ground when it shakes. As office buildings and high-rise apartments outfitted with seismic isolation become more commonplace, these structures are increasingly part of the world each of us lives in. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of the seismic isolation structures that provide us with safety and peace of mind, explain how the technology has been adopted for use beyond buildings to protect valuable assets through equipment seismic isolation, and take a behind-the-scenes look at how THK adapted its linear motion technology to develop its very own kind of seismic isolation.
Features of Seismic Isolation Structures for Buildings
roadly speaking, there are three types of structures used to protect buildings from earthquakes: seismic isolation, seismic damping, and earthquake-proofing. Let’s look at what makes each of them unique.
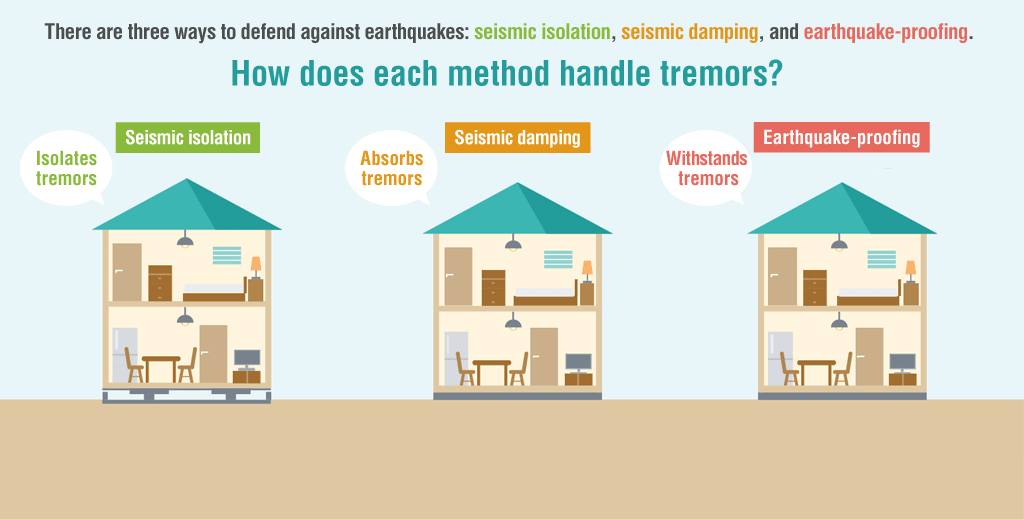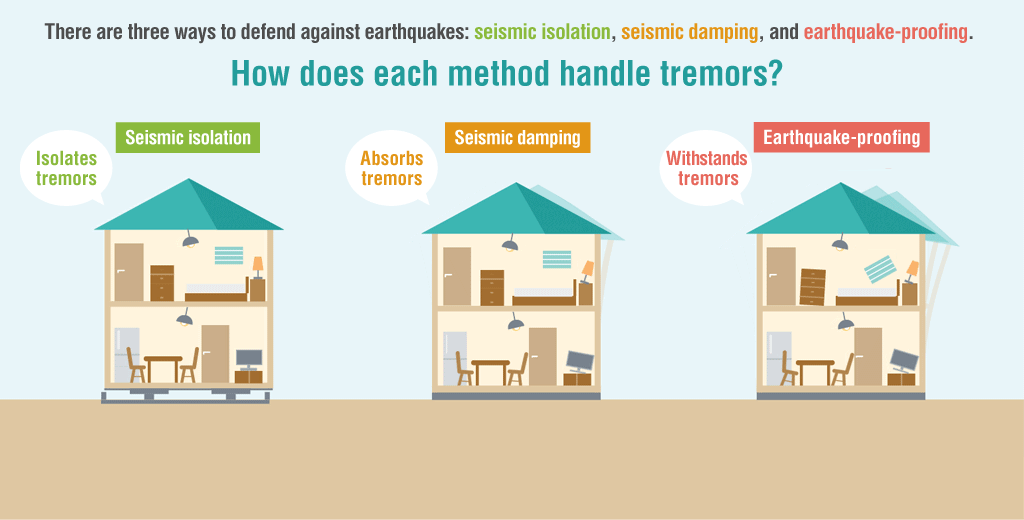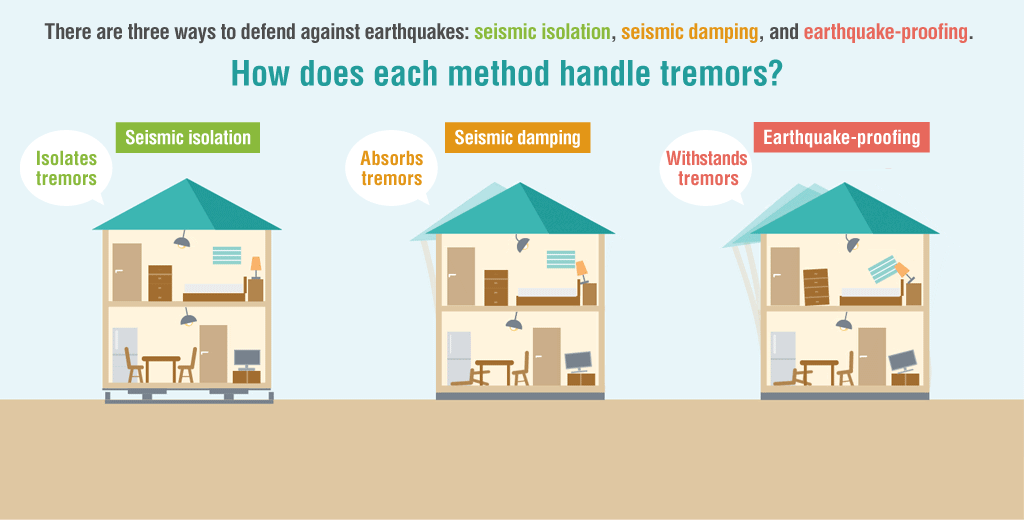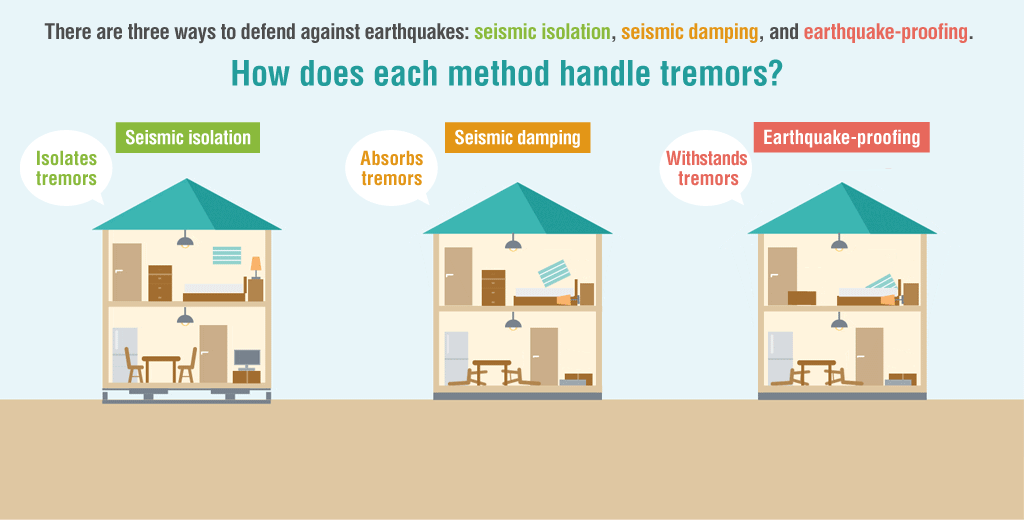
Seismic Isolation Deflects Tremors
Installing a seismic isolation system between a building and its foundation prevents seismic tremors from being directly transferred to the building by providing isolation from the ground.
Seismic Damping Absorbs Tremors
Buildings with these structures absorb earthquake tremors via built-in seismic damping materials such as weights and dampers. This technology is extremely effective for skyscrapers and other tall buildings, where shaking becomes more intense the higher up you go.
Earthquake-Proofing Withstands Tremors
Many homes in earthquake-prone regions have earthquake-proof structures strong enough to withstand tremors to the extent that the building doesn’t collapse and the residents can evacuate.
Comparing Seismic Isolation, Seismic Damping, and Earthquake-Proofing (at Seismic Intensity 6)
The table below compares seismic isolation, seismic damping, and earthquake-proofing structures to show how much of a difference a seismic isolation system makes for the inside of a building when a large-scale earthquake occurs.
Isolation vs. Seismic Damping vs. Earthquake-proofing
|
Seismic isolation |
Seismic damping |
Earthquake-proofing |
|
|
Likelihood of furniture falling over |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Likelihood of tableware and glasses shattering |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Likelihood of structural damage |
Extremely low |
Low |
High |
|
How tremors are handled |
Ground tremors are not transferred directly, so the building shakes less than the ground. |
Upper-story shaking is less than with earthquake-proofing, but it does not shake less than the ground does. |
Each floor of the building shakes more than the one below. |
Beyond Buildings: Seismic Isolation Scaled for Equipment
Seismic Isolation Systems Focused on Protecting Equipment
Seismic isolation systems for equipment protect works of art, societal assets, servers, and equipment from earthquake damage by isolating them from the floors on which they’re set and softening the intensity of tremors generated during earthquakes.
These systems have come to be regarded as an effective way to protect important cultural properties, works of art, servers, medical equipment, and other socially and commercially important assets from earthquakes. They offer protection that costs less and is both faster and easier to install than seismic isolation for entire buildings, especially when it comes to existing facilities.
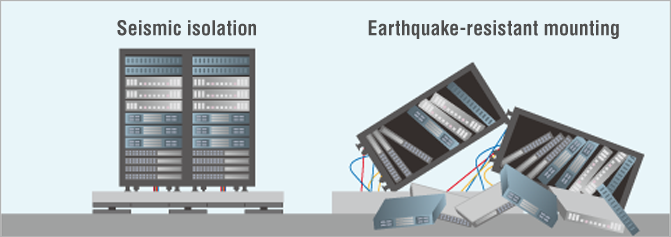
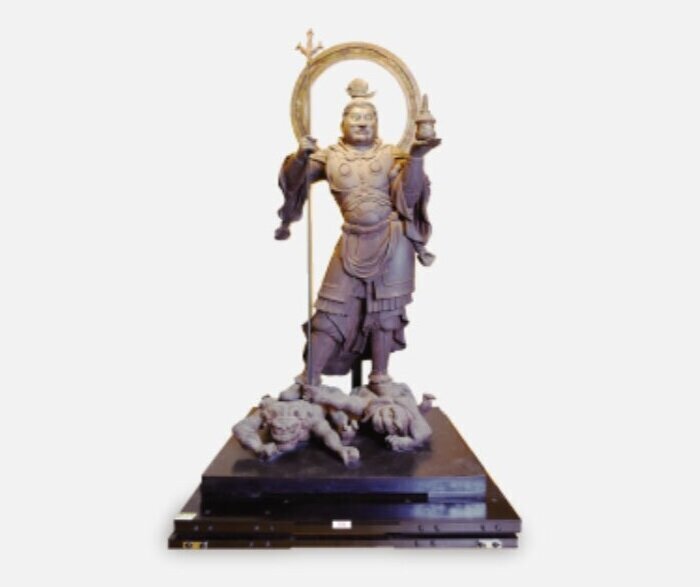
Seismic isolation systems can also be installed in specific locations to protect tremor-sensitive assets such as works of art, servers, and medical devices from earthquakes.
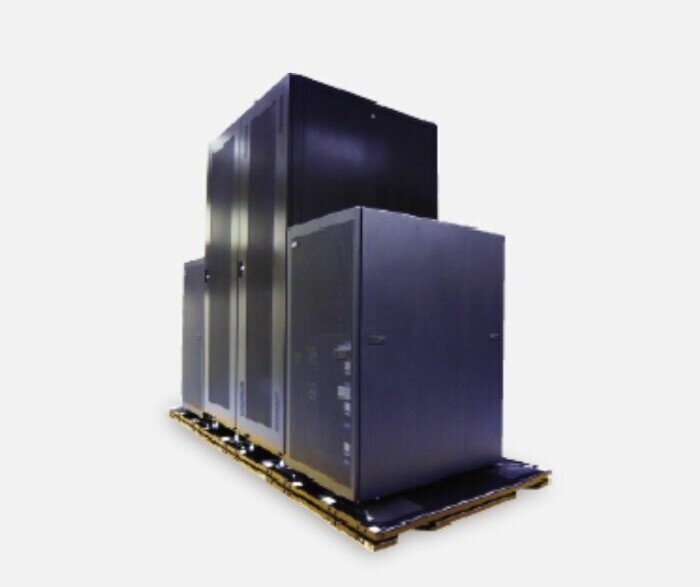
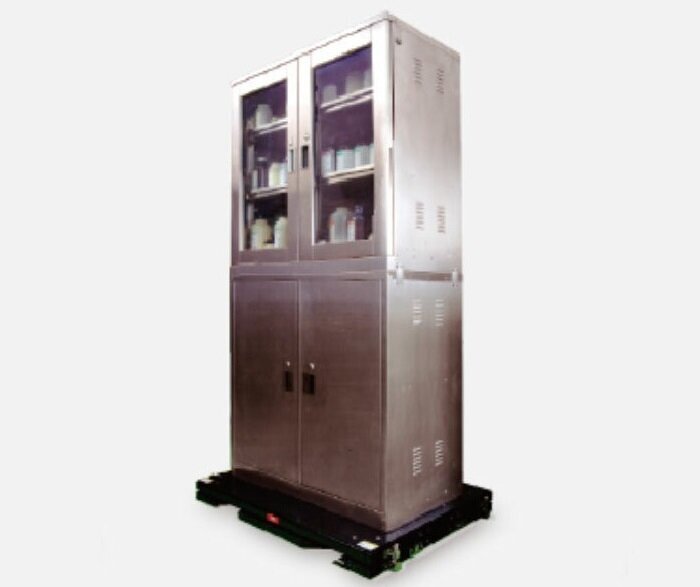



Seismically Isolating an Entire Floor
Comparing seismic isolation to earthquake-resistant mounting shows how much of a difference a seismic isolation system makes for the inside of a building during a large-scale earthquake.


Behind the Scenes: Developing Seismic Isolation for Safety and Peace of Mind
In 2001, THK established its ACE (Amenity Creation Engineering) Division, tasking it with “developing technology to realize creative living spaces for greater comfort.” As they adapted linear motion guide technology to an increasingly wide range of fields, it eventually struck them that seismic isolation structures were the best option for earthquake protection. It was at this moment that they decided to embark on developing and disseminating such seismic isolation technology.
But THK's development of seismic isolation structures began even before the ACE Division was established, springing from a conversation with a general contractor about the possibility of using low-friction rolling guides in seismic isolation systems. Then, just as the prospect of developing such a technology was beginning to take shape, the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake of 1995 struck, prompting the formation of the dedicated team that preceded the ACE Division and accelerating THK's decisive entry into the seismic isolation industry. Development did not go smoothly, however, as they were unsure if using an unmodified linear motion guide would really achieve seismic isolation, and they struggled with how to develop a product for construction use.
THK’s seismic isolation structure technology debuted as a seismic isolation system for buildings. At the time, laminated rubber was the mainstream seismic isolation solution for buildings, but the idea that a machine component like the linear motion guide could be adapted to attenuate tremors even further and provide even greater seismic isolation performance quickly garnered attention. For one thing, laminated rubber could only provide seismic isolation up to 10 floors, but when THK set out to develop its own seismic isolation system, it chose to challenge itself by asking the bold question: Why not aim for 20?
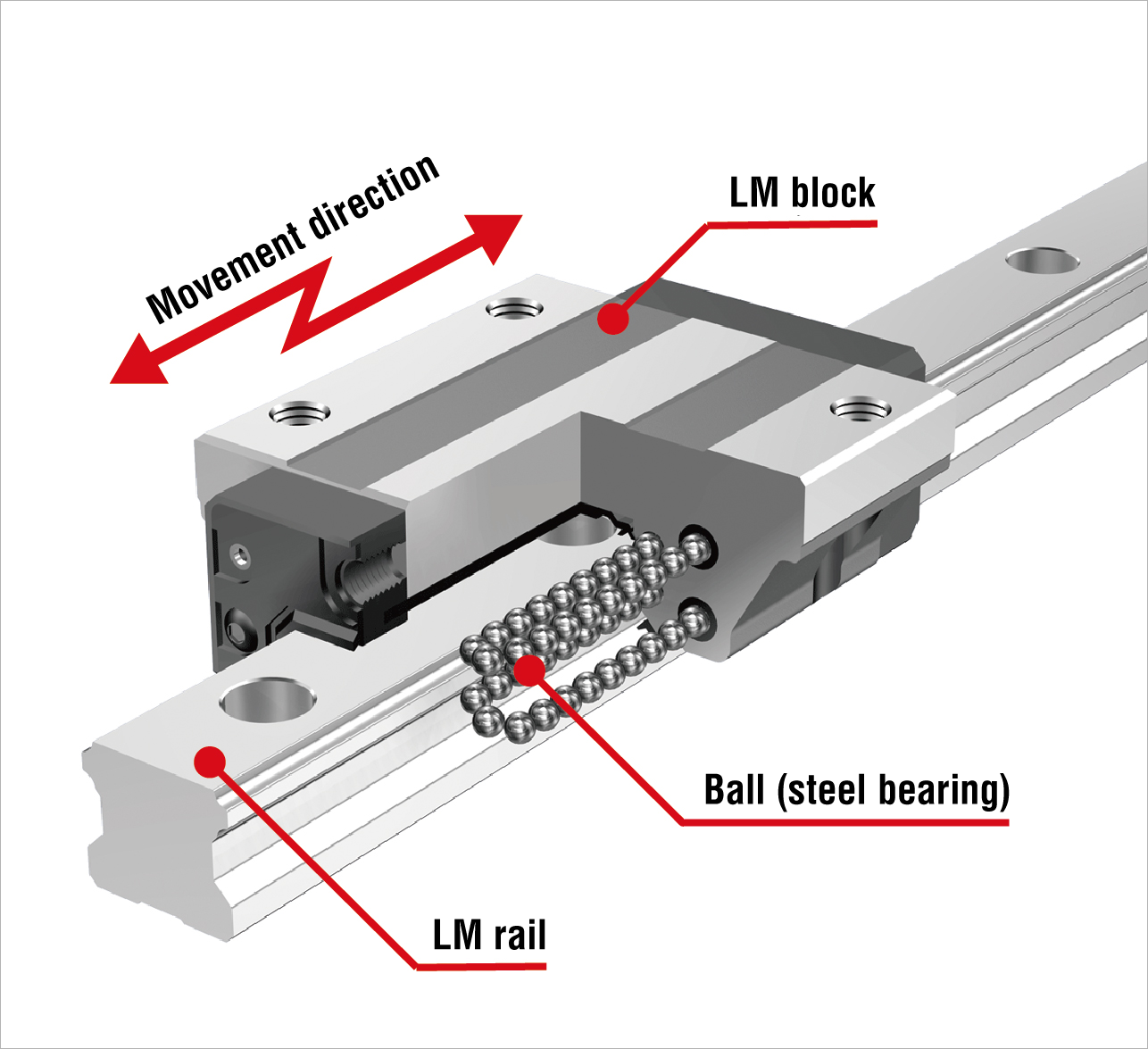
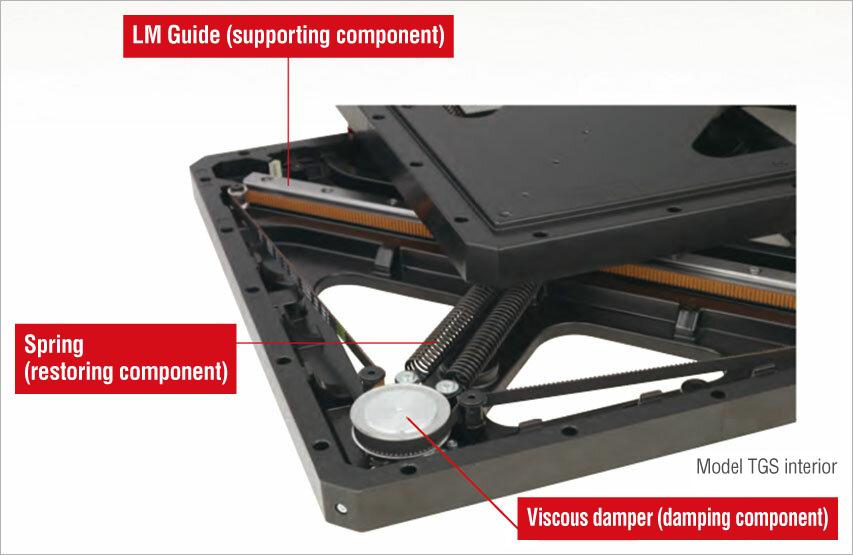
THK's seismic isolation structure deflects earthquake tremors using a mechanism composed of two LM Guide units arranged in a cross formation so that they can move in any direction based on seismic activity. If rolling technology is added to this mechanism to reduce friction, the structure can also be adapted for use in various types of seismically isolated buildings. Nowadays, this seismic isolation technology is utilized in applications ranging from single-family homes to pieces of equipment.
Today, there are about 4,000 buildings in Japan with seismic isolation, not counting single-family homes. One of the factors spurring the proliferation of these buildings is the fact that seismic isolation has proven effective during actual earthquakes. It has been confirmed, for example, that seismic isolation structures reduced the damage caused by the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake (1995), Great East Japan Earthquake (2011), and Kumamoto Earthquakes (2016). There have even been hospitals that were able to start seeing patients again right after an earthquake thanks to their being equipped with seismic isolation. Beyond keeping buildings safe, this ability to support sustained operations is another reason seismic isolation has attracted so much attention, especially from municipal governments and businesses that see it as part of a BCP (business continuity plan).

THK’s Seismic Isolation Structure: Maximum Seismic Isolation Born of Machine Component Technology
At Its Core, the Same LM Guide Used in Industrial Machinery Worldwide
The LM Guide technology at the heart of our seismic isolation modules uses rolling motion to produce linear motion with substantially reduced friction resistance. This results in smooth motion capable of deflecting seismic tremors. Since its development by THK in 1972, the LM Guide has spurred dramatic improvements in the performance of mechatronic equipment, and it is now the de facto standard for industrial equipment and machine tools around the world.
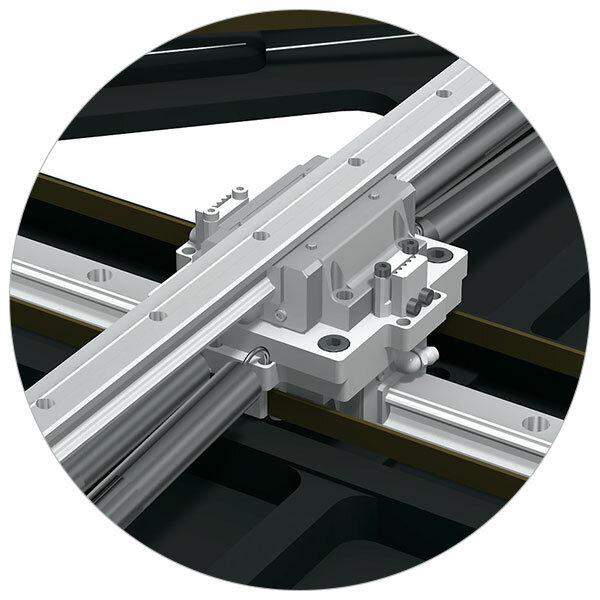

A Future of Safety with Seismic Isolation Structures
In the creation of our seismic isolation structure, THK has achieved its goal of applying the LM Guide technology we have cultivated to the task of providing safety and peace of mind in the face of earthquakes. When disaster strikes, our seismic isolation structure preserves people’s quality of life, contributes to business continuity, and protects valuable assets. It has a vital role to play in the creation of a better future. THK will continue to leverage its technological strength as a manufacturer of machine components to help create a sustainable society in which seismic isolation structures allow people to live without fear.
Comparison of Seismic Isolation, Seismic Damping, and Earthquake-Proofing
The table below shows how earthquake-proofing, seismic damping, and seismic isolation compare with one another, and the difference that having a seismic isolation system makes on an indoor environment during a large-scale earthquake.
Details about seismic isolation (THK seismic isolation website)
Download the seismic isolation catalog (THK seismic isolation website)
* This content is based on information that was released in Japanese on July 19, 2023.