May 21, 2025
Feb 18, 2026
Products
A Study in Rolling Guides: Sustaining Accuracy and Boosting Durability with Ball Splines
- Example of Use
- Column
- Product Introduction
- General Industrial Machinery
- Machine Tools
- Industrial Robots
- Precision Machinery / Instrument
- Electricity / Electronics
- Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment
- Automotive and Transportation Equipment
- Picking Robot
- Articulated Robot
- THK Online Services
- High Rigidity
- Pick&Place
- Labor Savings
- Non-Magnetic
- High Accuracy
- High Speed
- Ball Spline
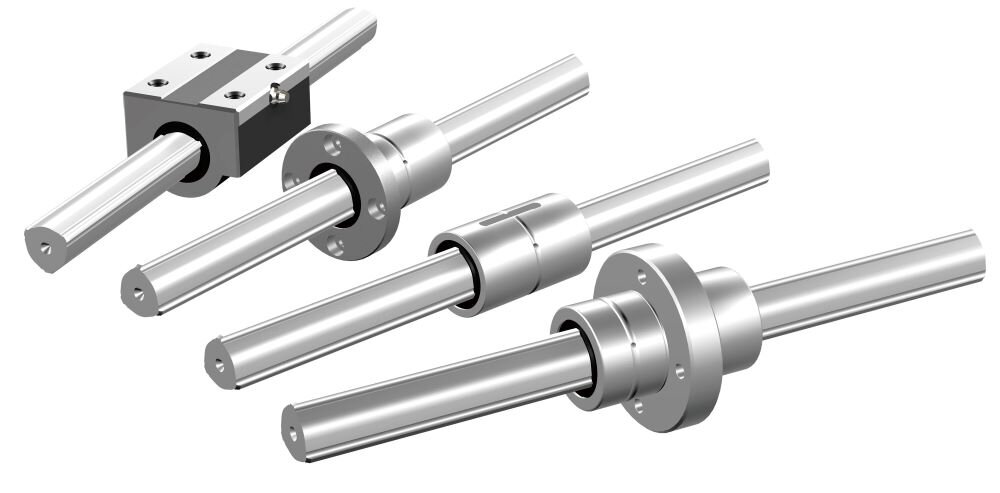

Linear motion guides are a critical part of what makes machines move. Because some applications require micron-level accuracy, any reduction in positioning accuracy has a large impact on product quality and production efficiency as well. This requires not only achieving a high level of accuracy but maintaining it as well. In this article, we’ll focus on the most common cause of reduced accuracy, wear, and look at ball splines that reduce it to keep accuracy high.
The Benefits of Rolling Guides
Several different types of linear guides are used in machines. These can broadly be divided into three groups: sliding guides, static pressure guides, and rolling guides.
Sliding Guides
As their name implies, these guides provide sliding motion thanks to lubricant contained between their moving parts and guide surfaces. These guides offer high rigidity and damping performance and are used for large processing machines. Their large contact surface creates a large amount of friction resistance, though, making them poorly suited to high-speed motion and high-accuracy positioning.
Static Pressure Guides
Static pressure guides utilize pressurized oil and air to keep their moving parts and guide surfaces from making contact. This lack of contact produces low friction resistance and reduces wear on this type of guide. The guide surfaces of static pressure guides have to be extremely accurate, however, requiring a manual scraping process to apply the right finish, which can make them difficult to utilize in some cases.
Rolling Guides
Rolling guides move using rolling elements (balls or rollers) placed between their moving parts and guide surfaces. This produces low friction resistance and makes them suited to high-speed motion. Additionally, if a preload is applied to one of these guides, it will be able to consistently provide long-term, high-accuracy performance.
While each type of guide has its merits, rolling guides are uniquely ideal for most of the places where a linear guide would be needed.
Reducing Wear with Rolling Guides! What Is a Ball Spline?
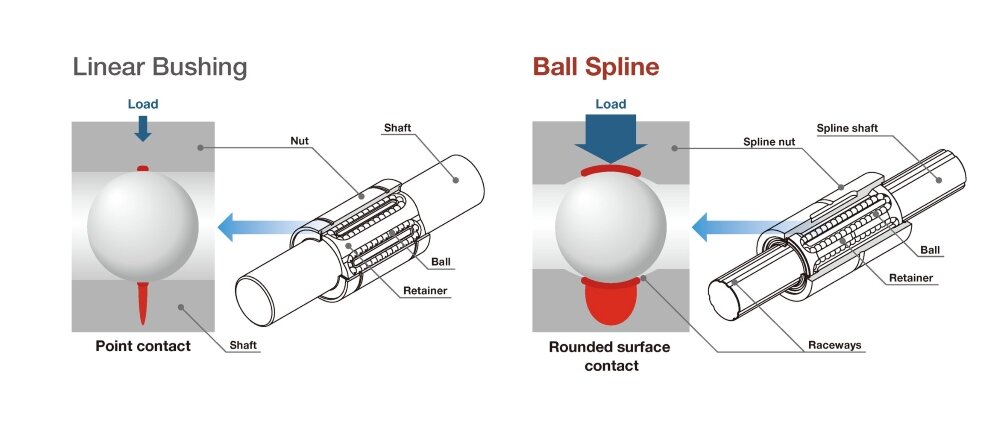
Linear bushings, used for the slide mechanisms in some machines, are one example of a rolling guide. They are used in combination with cylindrical LM shafts. Because the balls of a linear bushing make point contact with its LM shaft, these guides provide linear motion with minimal friction resistance. Being rolling guides, linear bushings can facilitate nimble motion as well. The point contact between linear bushing balls and the LM shaft is a double-edge sword, however, as it makes for a small contact surface area. As a result, these guides are not suited to moving while under a load, and bearing a load can actually accelerate wear.
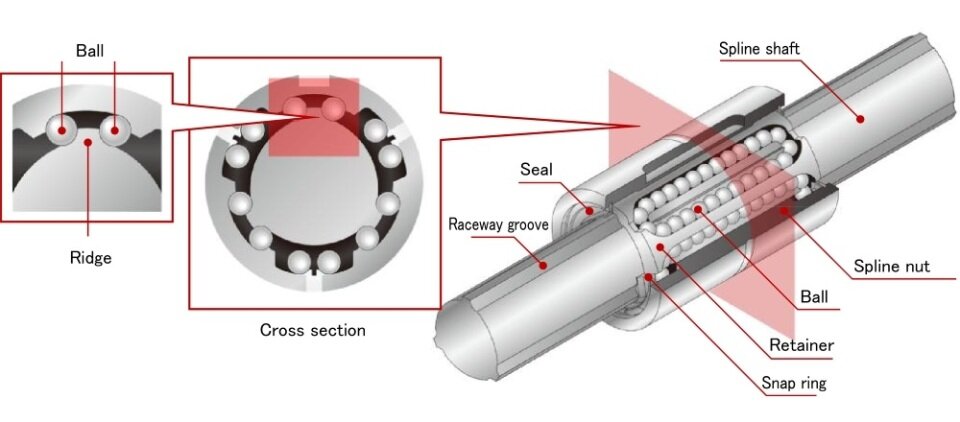
This is where the ball spline comes in. Raceway grooves increase the area of contact with the balls, giving ball splines large permissible loads that allow them to bear these heavier burdens. All of this means that ball splines are quite well-suited to moving while under a load. Compared to a linear bushing under the same load, a ball spline will take longer to wear down and will be able to operate over a longer period.
Why Do Production Floors Choose the Ball Spline?
The ball splines used on countless production floors offer three main advantages.
Sustained accuracy: The rolling mechanism prevents backlash and maintains a high degree of accuracy over the long term.
Increased durability: The low-friction structure reduces wear and extends service life.
Reduced costs: Reducing how frequently parts need to be replaced also lowers maintenance costs.
Let’s take a look at some example applications that highlight these advantages.
Eliminating Backlash for Long-Term, High-Accuracy Performance!
One of the critical factors in maintaining machine accuracy is reducing backlash.
A sliding guide requires a certain amount of clearance between its nut and its shaft to function. This gap introduces play between the components, however, which reduces the guide’s accuracy. While one might try to reduce the clearance inside the sliding guide to improve accuracy, this could ultimately backfire by making it impossible for the guide to move at all.
Rolling guides, on the other hand, offer more accurate linear motion than sliding guides. For ball splines in particular, accuracy can be even further enhanced and maintained over the long term by applying enough of a preload to eliminate backlash altogether. Such large preloads are made possible by the increased contact area offered by a ball spline’s raceway grooves.
Example application: Semiconductor manufacturing equipment
A customer was using sliding guides for the sliding portions of their equipment, which led to issues with wear. This wear widened the gap between guide components, raising concerns of reduced rigidity. By switching to ball splines with their low-friction structure, the customer benefited from reduced component wear, resolved concerns around reduced rigidity, and saw their equipment run with greater stability.
Greater Durability for Fewer Replacements and Lower Costs!
Having to frequently replace machine components makes increased maintenance costs and downtime unavoidable. Ball splines, however, remedy this with longer service life made possible by their large permissible loads. Because they don’t need to be replaced as often, they reduce maintenance and total costs considerably. The durability of ball screws can be enhanced even further with proper lubrication.
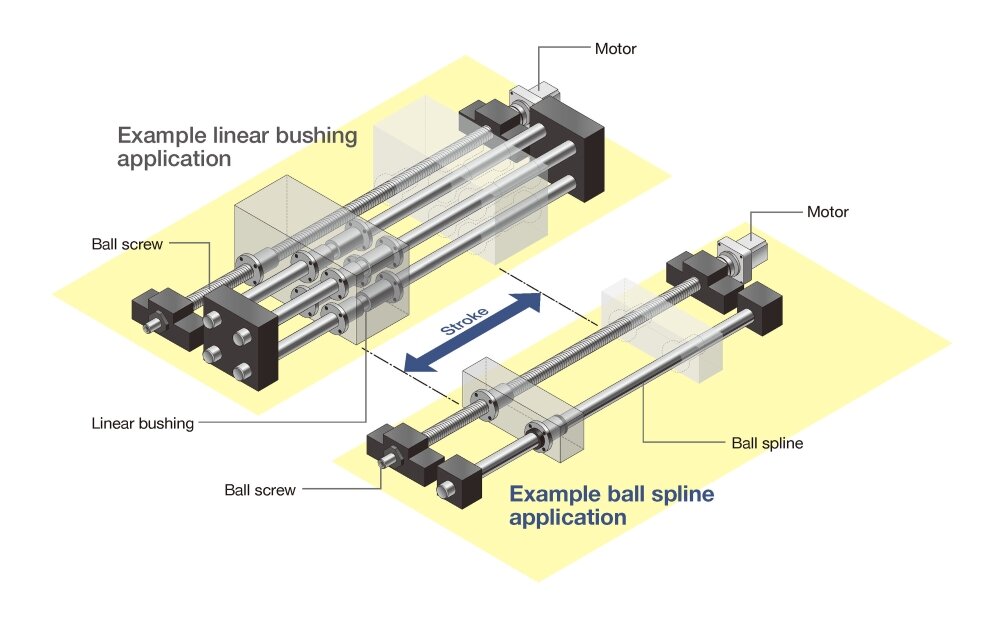
Additionally, ball splines can handle torque with one shaft, which makes it possible to use fewer and smaller peripheral components than required by linear bushings. This too contributes to cost savings.
Example application: Automatic wrapping machines
The customer had been using linear bushings for the lifting and lowering part of their equipment, but these weren't rigid enough in places subject to moment loads.
By switching to ball splines to capitalize on their larger area of contact and permissible load, however, the customer saw reduced friction and increased rigidity. This ultimately extended the life of their equipment and allowed for less frequent maintenance.
High Accuracy and Enhanced Durability for a Wide Array of Industries
This time, we took a closer look at the advantages of using ball spline rolling guides. Because ball splines maintain a high level of accuracy and offer enhanced durability, we believe they contribute to more stable machine operation and reduced operating costs. Even now, they are in use in a wide range of settings that demand both accuracy and durability, from machine tools and industrial robots to medical devices and more.
Please contact THK for all your equipment concerns and support needs.
* This content is based on information that was released in Japanese on May 21, 2025.