Apr 26, 2023
Products
Linear Motion Products That Determine Machine Tool Performance
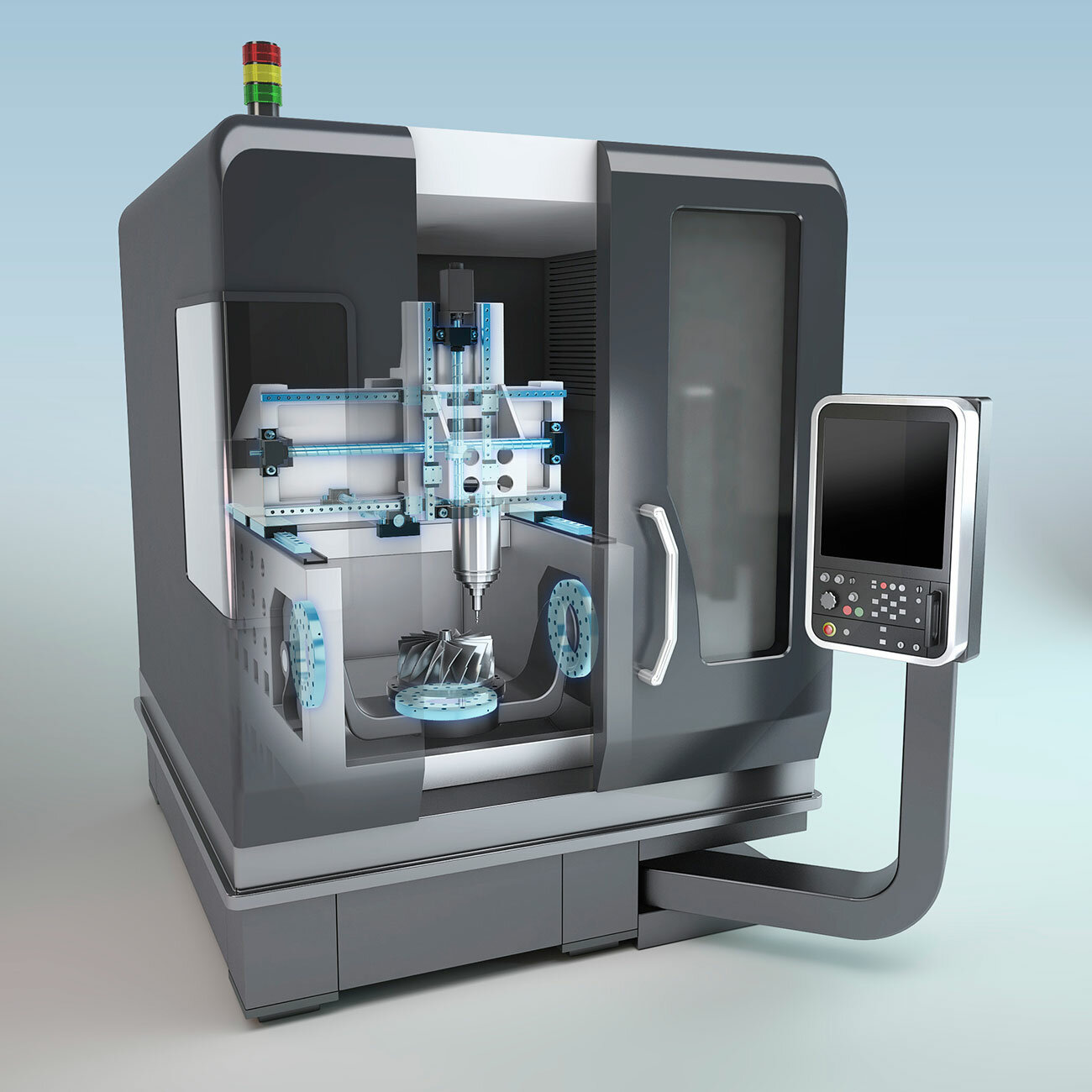

Manufacturing generally refers to the entire process of creating a product, starting with design and including selection. Throughout the manufacturing industry's production processes, appropriate control of product quality is crucial to meeting customers’ needs. Let's take a look at linear motion products that have a large impact on machine tool performance.
The Machine Tools That Support Manufacturing
Machine tools, called “mother machines,” are devices that process metal precisely into complex shapes with high speed and accuracy. They are used to make various products and parts, from things as small as cameras and clocks to those as large as automobiles and aircraft, and they play a key role in supporting our daily lives from behind the scenes. As machine tools increasingly take on a 5-axis (multi-axis) design to handle combined machining, various developments are being promoted to meet the demand for increased production efficiency.
In the world of manufacturing, linear motion products such as the LM Guide are indispensable to reach the full performance capabilities of machine tools.
Desired Specifications
As previously stated, machine tools process things precisely at high speeds. Accordingly, linear motion products that enable high-precision, high-speed movement are vital as guides for tooling and tables. These products must also have a high degree of rigidity to suppress chatter* from cutting recoil, and they must be durable against coolant and shavings.
* Chatter is an umbrella term for the vibrations continuously generated during cutting processes.
High Rigidity and Contamination Protection
High Rigidity
Rigidity is a measure of a thing’s resistance to warping due to an applied force. If this is lacking in a machine tool, it will yield to recoil from processing, and the precision of the machined material will suffer. For example, picture holding a pencil lightly and drawing a straight line on a piece of paper. If you try to press the tip of the pencil to the paper, you can’t support against the recoil because your hand isn’t gripping the pencil tightly. You will probably end up drawing a wobbly line. When processing workpieces, tooling works the same way that a pencil does. If the components that support tooling yield to recoil and are warped, they can’t process things with precision. Thus, the components that support these tools, namely, the LM Guide, require a high degree of rigidity.
Contamination Protection
The internal components of machine tools must be able to withstand a harsh environment of various coolants meant to improve machining performance, as well as atomized machining dust. Without exception, the LM Guide offers a large number of contamination protection options.
If the contamination prevention performance of an LM Guide inside a machine tool is lacking, shavings and coolant can get inside the block and cause significant damage to the circulating balls and circulation parts. It is important to be aware of this as, depending on the situation, it can cause overall damage. We recommend considering contamination protection options for LM Guide applications in machine tools and in other harsh environments as well.
THK Product Lineup
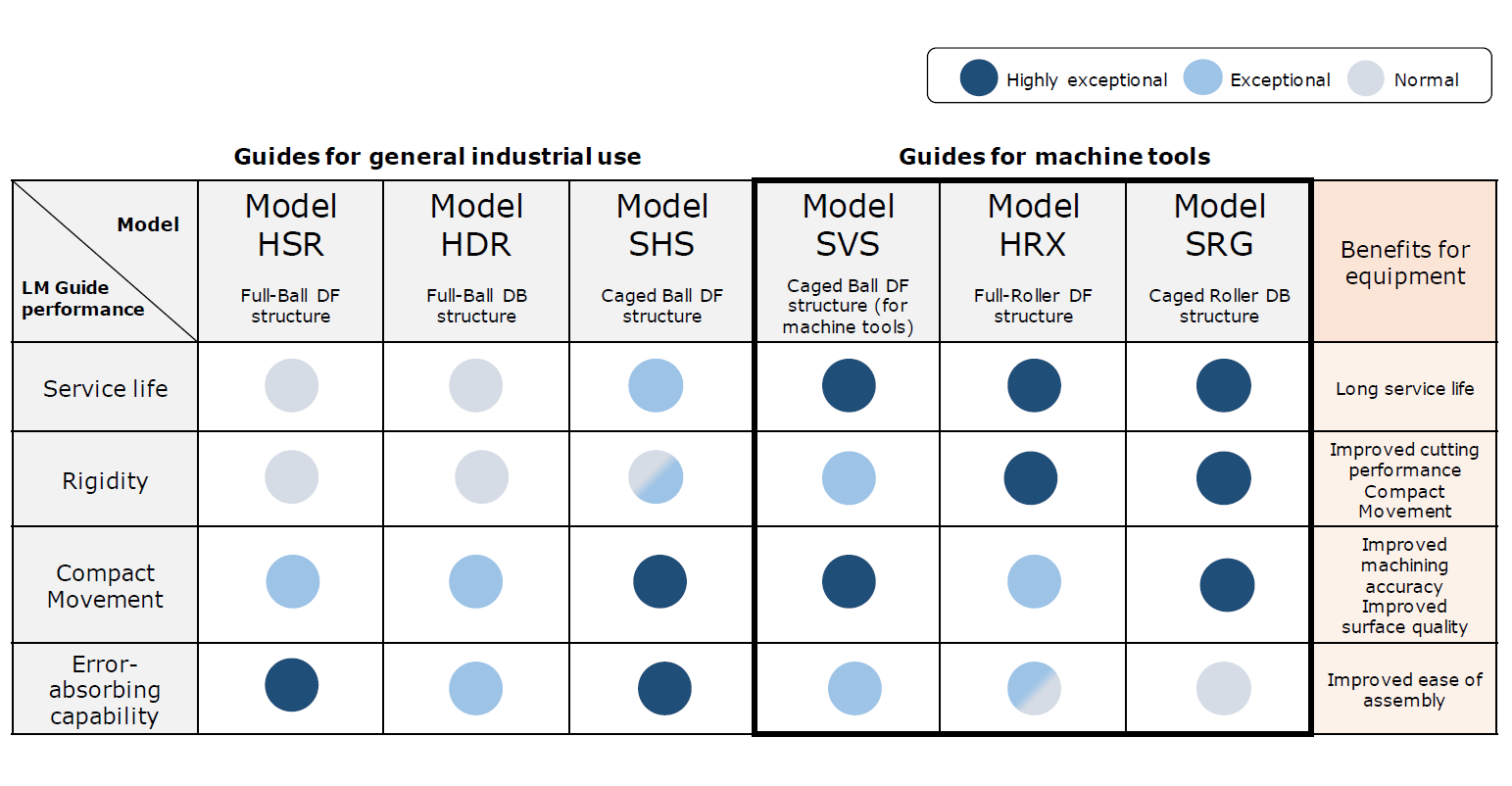
THK offers ultra-high load LM Guide products for machine tools in the form of Caged Ball models SVS and SVR, as well as the Full-Ball Model NR. Of all LM Guide products that utilize balls as their rolling element, these types offer the highest rigidity and load capacity. For the raceways, they use a deep circular arc groove with a curvature similar to the ball diameter. As the load increases, more of the surface comes in contact with the balls, which gives these guides a large load capacity and improves damping.
Various options, including end seals, inner seals, side seals, Laminated Contact Scraper LaCS, protectors, side scrapers, and GC caps, are available to accommodate various service environments.

When even higher rigidity is required, we recommend the Caged Roller LM Guide SRG, which uses rollers that are more rigid and have higher load resistance than balls for its rolling element. This higher rigidity is due to the overall length of the rollers being 1.5 times their diameter. The Model SRG is also available with an ultra-long block type that is 50% longer than a standard block and has a 50% greater load rating. We hope you will consider this ultra-long block type when designing high-load equipment.
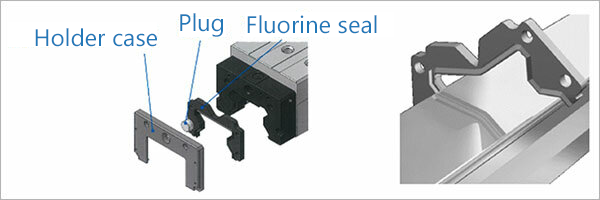
In addition to end seals, inner seals, said seals, Laminated Contact Scraper LaCS, protectors, side scrapers, and GC caps offered as options for the model type above, the high chemical resistance fluorine seal FS is also available for this model.
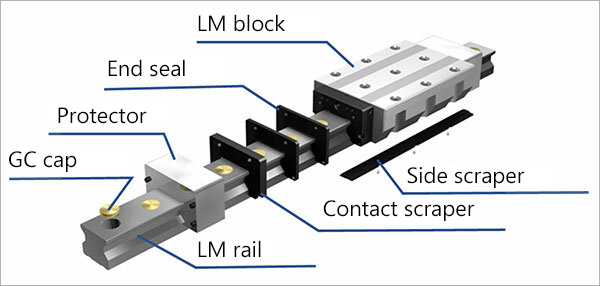
The fluorine seal offered exclusively for the Model SRG uses a highly chemical-resistant fluorine rubber that was developed to withstand environments with aggressive coolants. One of the features of the seal is that it can be added to or removed from the top surface of an LM rail, making it easy to add or replace to strengthen contamination protection. Because the seal can be mounted onto equipment covers as well, it can offer even greater contamination protection.
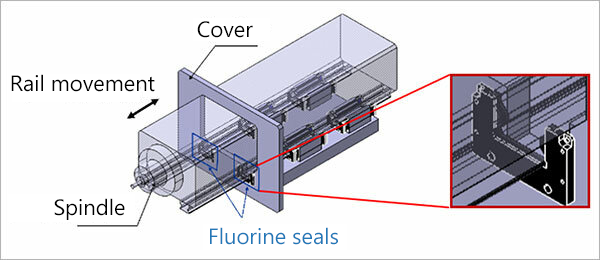
Additionally, the Full-Roller type roller guide Model SRG-G has been newly developed with exceptional robustness* for enhanced durability in environments with even more debris. Even for a Full-Roller design, this model achieves reduced roller skew and stable motion. With the same dimensions as the caged type, it covers the entire range of the caged type lineup so you can select whichever type is suited to each circumstance. For example, in a five-axis machine, the machining axis used closest to the workpiece can utilize a Full-Roller type guide while all other axes utilize caged type ones.
* Robustness is a thing’s quality to resist the effects of external forces.
Uses of Different Models
As mentioned previously, roller guide models excel in rigidity and basic load rating beyond other model types, and are thus utilized in many devices that require rigidity, such as machine tools, as well as for the transfer of heavy loads. On the other hand, this high rigidity magnifies the effects of misalignment, making a highly accurate mounting surface necessary. As a result, it is more difficult to design peripheral components when using roller guides than it is when using other types of LM Guide.
Not all of a machine's moving parts require an LM Guide with such high rigidity. For example, loader parts require speed more than rigidity, and emphasis is placed on making them light for that reason. Even within the same piece of equipment, performance should be considered based on the application when selecting each component.
This concludes our case study of LM Guide selection for machine tools.
In these product blogs, we will continue to share more information through the lens of our products.
* This content is based on information that was released in Japanese on April 26, 2023.
THK Online Services features technical support tools for the THK product catalog and instruction manuals, CAD data, product FAQ, technical materials, product selection, and service life calculation.
* Those who do not have an ID must register for a free account before using.