Nominal Life
Calculating the Nominal Life
The nominal life (L10) is obtained from the following formula using thebasic dynamic load rating (C) and the load applied to the RW (PC).

| L10 | Nominal life1(rev) |
|---|---|
| C | Basic dynamic load rating2 (N) |
| PC | Dynamic equivalent radial load (N) |
Calculating the modied nominal life
During use, the Model RW may be subjected to vibrations and shocks as well as uctuating loads, which are difcult to detect. In addition, the operating temperature will have a decisive impact on the service life. Taking these factors into account, the modied nominal life (L10m) can be calculated according to the following formula.
Modied Factor α

| α | Modied Factor |
|---|---|
| fT | Temperature factor |
| fW | Load factor |
Modied Nominal Life L10m
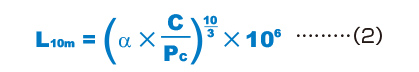
| L10m | Modified nominal life1 (rev.) |
|---|---|
| C | Basic dynamic load rating2(N) |
| PC | Dynamic equivalent radial load (N) |
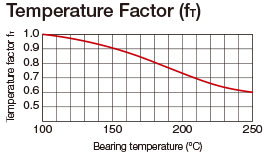
- Note) The normal service temperature is 80°C or below.If the product is to be used at a higher temperature, contact THK.
- 1Nominal life is determined by load calculations assuming adequate lubrication and ideal assembly conditions. Service conditions such as rocking motion or low-speed motion can have an impact on lubrication status. Consult with THK about the calculation of service life under rocking motion or low-speed motion.
- 2The basic dynamic load rating (C) indicates the radial load for which the nominal life is one million rotations when a group of identical Model RW units independently operate under that load when it is applied with a constant direction and magnitude. The basic dynamic load ratings (C) are indicated in the specification tables.
fw : Load factor
Machines that perform rotary movements are often subjected to vibration and impact during operation. It is difficult to accurately identify the cause of vibration from a motor, gears, or other drive components, or of impact arising from frequent starts and stops.In the event of excessive vibration or impact, divide the basic dynamic load rating (C) by the corresponding load factor, using the empirically obtained figures in Table1 as guidelines.
| Usage conditions | fw |
|---|---|
| With smooth motion and no impacts |
1 to 1.2 |
| With normal motion |
1.2 to 1.5 |
| With severe impacts |
1.5 to 3 |
Calculating the Service Life Time
For Rotary Motion
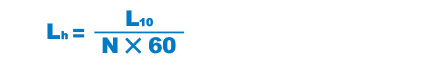
| Lh | Service life time (h) |
|---|---|
| N | Revolutions per minute (min-1) |
- * If rotated continuously, significant heat may be generated depending on the rotation speed. Consult with THK about the rotation speed.
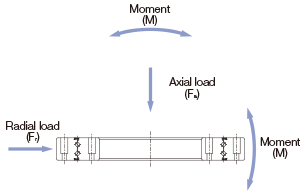
Dynamic Equivalent Radial Load PC
The dynamic equivalent radial load of the Model RW is obtained from the following formula.
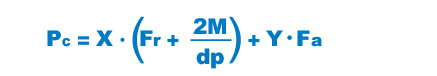
| PC | Dynamic equivalent radial load (N) |
|---|---|
| Fr | Radial load (N) |
| Fa | Axial load (N) |
| M | Moment (N・mm) |
| X | Dynamic radial factor |
| Y | Dynamic axial factor |
| dp | Roller pitch circle diameter (mm) |
| Category | X | Y |
|---|---|---|
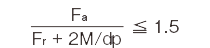 |
1 | 0.45 |
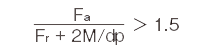 |
0.67 | 0.67 |
- ●When Fr = 0 (N) and M = 0 (N・mm), perform the calculation assumingthat X = 0.67 and Y = 0.67.
- ●For service life calculation with a preload taken into account, contact THK.