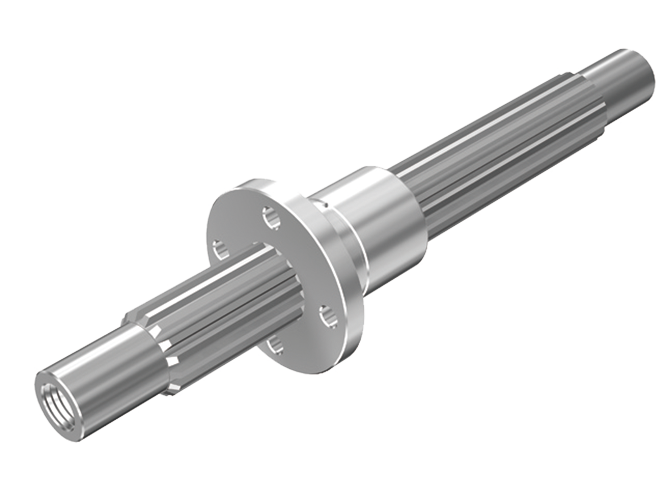
Spline Nut
Spline Nut Models DPM and DP are low-price bearings that are made of a special alloy formed by die casting, and they use highly accurate spline shafts as the core. Unlike conventional machined spline nuts, the sliding surface of these models maintains a skin layer formed in the rolling process, thus achieving high wear resistance.
The surface of the spline shafts to be used in combination with the nuts is hardened through rolling and is mirror-finished. As a result, smooth sliding motion is achieved.
The specially designed teeth of the spline have large contact areas in addition to concentricity, which enables the shaft to automatically establish the center as a torque is applied. Therefore, the teeth demonstrate stable performance in transmitting torque.
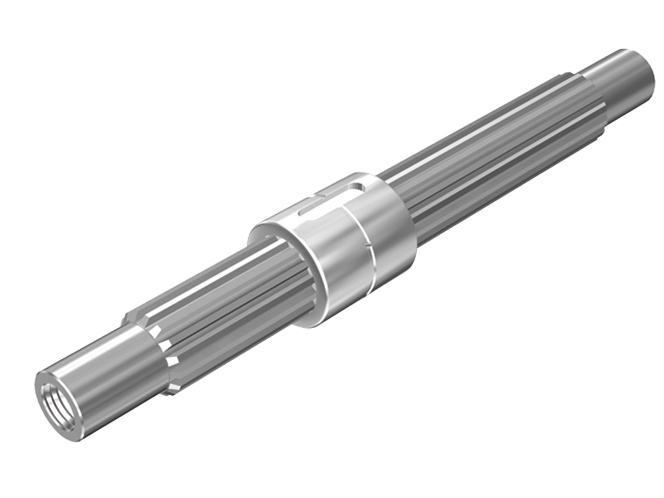
Types
Highlight feature tags
- Wear resistance
- Flanged type
- Cylindrical type
Search products by various conditions
Features
Structure and Features
Spline Nut Models DPM and DP are low price bearings that are made of a special alloy (see High Strength Zinc Alloy) that are formed by die casting and use highly accurate spline shafts as the core. Unlike conventional machined spline nuts, the sliding surface of these models maintains a chill layer formed in the rolling process, thus achieving high wear resistance.
The surface of the spline shafts to be used in combination with the nuts is hardened through rolling and is mirror-finished. Accordingly, smooth sliding motion is achieved.
The specially designed teeth of the spline have large contact areas, as well as concentricity, which enable the shaft to automatically establish the center as a torque is applied. Therefore, the teeth demonstrate stable performance in transmitting a torque.
Features of the Special Rolled Shafts
Dedicated rolled shafts with standardized lengths are available for the Spline Nut.
Increased Wear Resistance
The shaft teeth are formed by cold gear rolling, and the surface of the tooth surface is hardened to over 250 HV and mirror-finished. As a result, the shafts are highly wear resistant and achieve significantly smooth motion when used in combination with nuts.
Improved Mechanical Properties
Inside the teeth of the rolled shaft, a fiber flow occurs along the contour of the tooth surface of the shaft, making the structure around the teeth roots dense. As a result, the fatigue strength is increased.
Additional Machining of the Shaft End Support
Since each shaft is rolled, additional machining of the support bearing of the shaft end can easily be performed by lathing or milling.
High Strength Zinc Alloy
The high strength zinc alloy used in the spline nuts is a material that is highly resistant to seizure and wear and has a high load carrying capacity. Information on mechanical properties, physical properties, and wear resistance is presented below.
*The figures shown are target values—these figures are not guaranteed.
Mechanical Properties
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Tensile strength |
275 N/mm2 to 314 N/mm2 |
|
Tensile yield |
216 N/mm2 to 245 N/mm2 |
|
Compressive |
539 N/mm2 to 686 N/mm2 |
|
Compressive yield |
294 N/mm2 to 343 N/mm2 |
|
Fatigue strength |
132 N/mm2 ×107 (Schenk bending test) |
|
Charpy impact |
0.098 N・m/mm2 to 0.49 N・m/mm2 |
|
Elongation |
1 % to 5 % |
|
Hardness |
120 HV to 145 HV |
Physical Properties
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Specific gravity |
6.8 |
|
Specific heat |
460 J/(kg・K) |
|
Melting point |
390 ℃ |
|
Thermal expansion coefficient |
24×10-6 |
Wear Resistance
|
Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Test piece rotational speed |
185 min-1 |
|
Load |
392 N |
|
Lubricant |
Dynamo oil |

Clearance in the Rotation Direction
Clearance in the rotational direction : α≦20' MAX