Selecting a Spherical Plain Bearing
When selecting a Spherical Plain Bearing, follow the instructions below while referring to the basic dynamic load rating (C) and the basic static load rating (C0) indicated in the corresponding specification table, as a measuring stick.
Spherical Plain Bearing Service Life G
The basic dynamic load rating (C) is used to calculate the service life when the bearing oscillates under a load.
The basic dynamic load rating is calculated based on the contact surface pressure of the spherical sliding section.
The Spherical Plain Bearing service life G is expressed in the total number of rocking motions until it becomes impossible for the bearing to perform normal operation due to the increase in the radial clearance or in the temperature of the bearing as a result of wear on the spherical sliding section.
Since the bearing service life is affected by various factors such as the material of the bearing, magnitude and direction of the load, lubrication conditions and sliding speed, the calculated value can be used as an empirical, practical value.
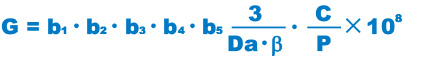
| G | Bearing service life (total number of rocking motions or total number of revolutions) |
|---|---|
| C | Basic dynamic load rating (N) |
| P | Equivalent radial load (N) |
| b1 | Load direction factor (see Table1 ) |
| b2 | Lubrication factor (see Table1 ) |
| b3 | Temperature factor (see Table1 ) |
| b4* | Dimension factor (see Fig.1 ) |
| b5 | Material factor (see Fig.2 ) |
| Da | Spherical diameter (see the specification table) (mm) |
| β | Oscillation half angle (degree) (for rotary motion, β=90°) |
- * If Da (spherical diameter) is 40 or less, use b4=1.
| Type | b1 | b2 | b3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load direction |
Regular lubrication |
Temperature °C | ||||||
| Fixed | Alter- nating |
Not pro- vided |
Pro- vided |
‒30 | +80 | +150 | ||
| +80 | +150 | +180 | ||||||
| Spher- ical Plain Bear- ing |
Without seal |
1 | 5 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 |
| With seal |
1 | 5 | 0.08 | 1 | 1 | - | - | |

Equivalent Radial Load
The Spherical Plain Bearing is capable of receiving a radial load and a thrust load simultaneously. If the magnitude and direction of the load applied are constant, the equivalent radial load is obtained from the following equation.

| P | Equivalent radial load (N) |
|---|---|
| Fr | Radial load (N) |
| Fa | Trust load (N) |
| Y | Thrust load factor (see Table2 ) |
| Fa/Fr≦ | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrust load factor (Y) | 0.8 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 3 |
Static Safety Factor fS
If the Spherical Plain Bearing is to be used under a stationary load or in slight rocking motion, select a model using the basic static load rating (C0) as a guide. The basic static load rating refers to the stationary load that the bearing can receive without damaging the bearing and without causing permanent deformation that would prevent smooth motion.
In general, set the safety factor at three or greater taking into account the rigidity of the shaft and thehousing.

| fS | Static safety factor |
|---|---|
| C0 | Basic static load rating |
| P | Equivalent radial load |
pV Value
The permissible sliding speed at which the Spherical Plain Bearing can be used varies depending on the load, lubrication conditions and cooling status. The recommended pV value for continuous motion under a load applied in a constant direction is calculated as follows.

If the Spherical Plain Bearing performs adiabatic operation or the load direction changes, the heat produced on the sliding surface easily radiates. Therefore, it is possible to set a higher pV value.
The contact surface pressure (p) of the Spherical Plain Bearing is obtained from the following equation.

| p | Contact surface pressure (N/mm2) |
|---|---|
| P | Equivalent radial load (N) |
| Da | Spherical diameter (see the specification table) (mm) |
| B | Outer ring width (see the specification table) (mm) |
The sliding speed is calculated as follows.

| V | Sliding speed (mm/sec) |
|---|---|
| β | Oscillation half angle (degree) |
| f | Number of rocking motions per minute (min-1 ) |
The Spherical Plain Bearing can be used at sliding speed of up to 100 mm/sec in oscillating motion, or up to 300 mm/sec in rotary motion in favorable lubrication status.