Designing the Guide System
THK offers various types of LM Guides in order to meet diversifi ed conditions. Supporting ordinary horizontal mount, vertical mount, inverted mount, slant mount, wall mount and single-axis mount, the wide array of LM Guide types makes it easy to achieve a linear guide system with a long service life and high rigidity while minimizing the required space for installation.
It is necessary to consider the position in the LM block where the grease nipple or the piping joint should be attached according to the mounting orientation.
If the mounting orientation is other than horizontal use, the lubricant may not reach the raceway completely. Be sure to let THK know the mounting orientation and the exact position in each LM block where the grease nipple or the piping joint should be attached.
Even with an LM Guide with seals, the internal lubricant gradually seeps out during operation. Therefore, the system needs to be lubricated at an appropriate interval according to the conditions.
For the mounting orientation and the lubrication, see Conditions of the LM Guide and Lubrication, respectively.
Examples of Arrangements of the Guide System
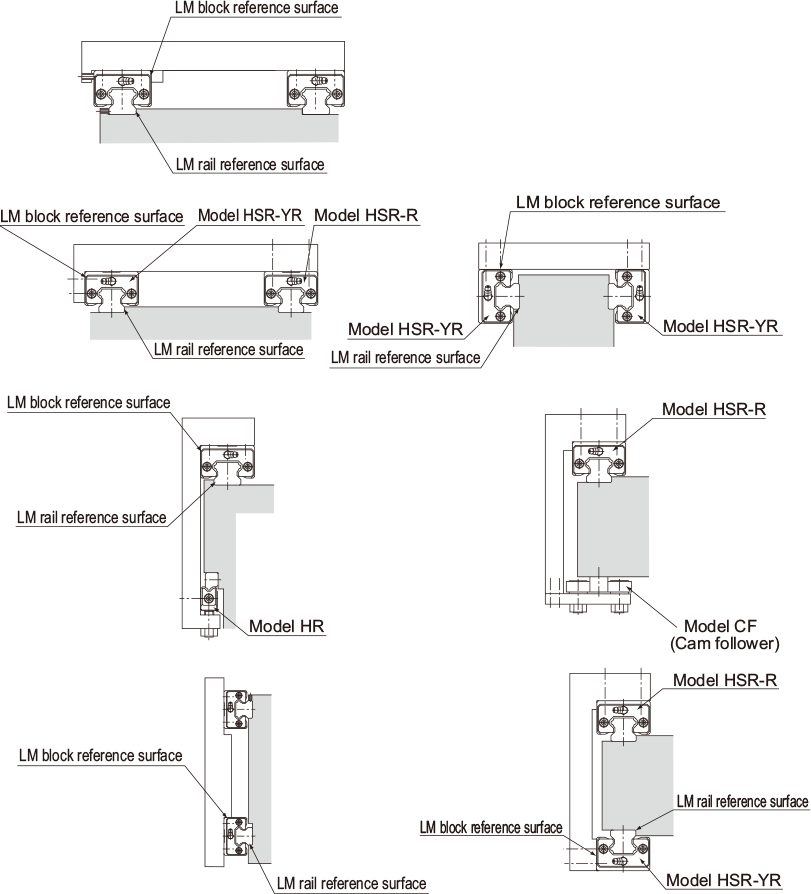
The following are representative guide systems and arrangements when installing the LM Guide. (For indication of the reference surface, see Marking on the Master LM Guide and Combined Use )
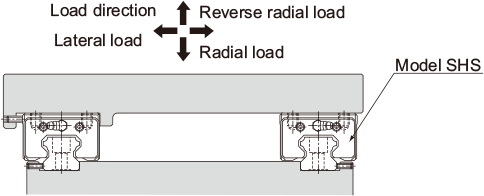
| Double-rail configuration when high rigidity is required in all directions | |
|---|---|
 |
|
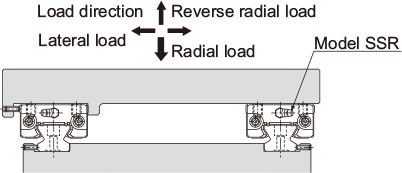
| Double-rail configuration when high rigidity is required in the radial direction | |
 |
|
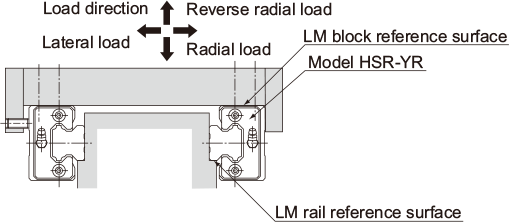
| When high rigidity is required in all directions and the installation space is limited in height | |
 |
|
| Single-rail configuration | |
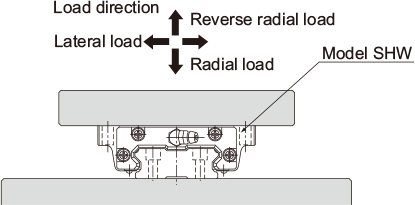 |
|
| When the minimum possible height of the equipment is allowed (Adjustable preload type) | |
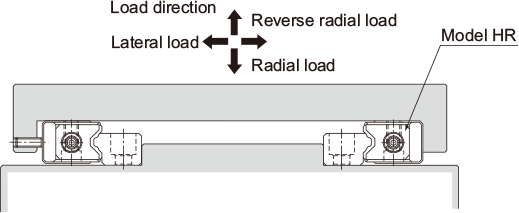 |
|
| When a medium load is applied and the mounting surface is rough (Preload, self-adjusting type) | |
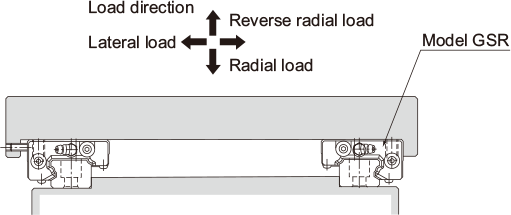 |
|
| Single-rail configuration | Triple-rail configuration |
 |
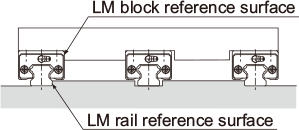 |
| Double-rail configuration | |
 |
|
| Multi-rail configuration | |
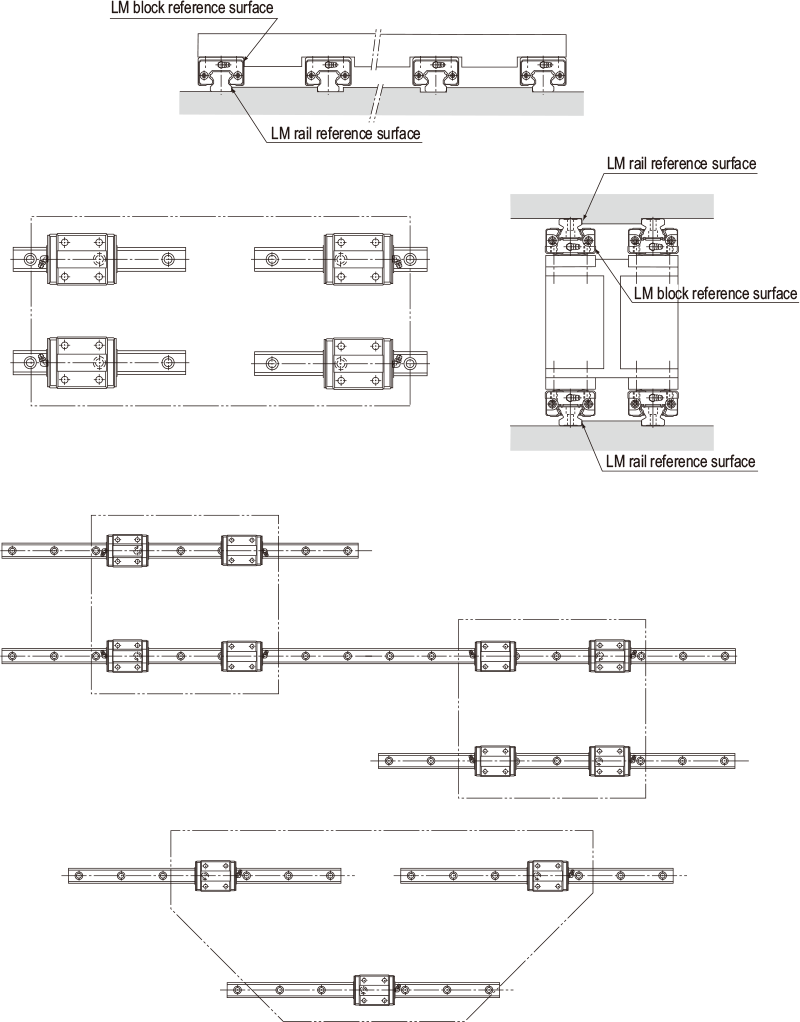 |
|
Method for Securing an LM Guide to Meet the Conditions
LM Guides are categorized into groups of types by mounting space and structure: a group of types to be mounted with bolts from the top, and another of types to be mounted from the bottom. LM rails are also divided into types secured with bolts and those secured with clamps (model JR). This wide array of types allows you to make a choice according to the application.
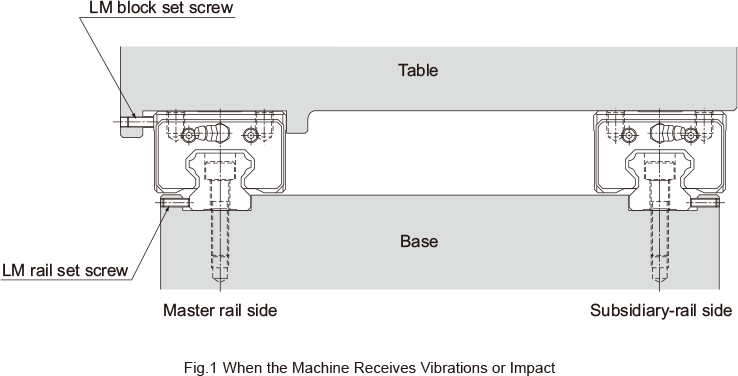
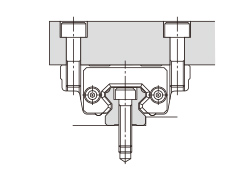
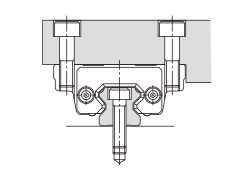
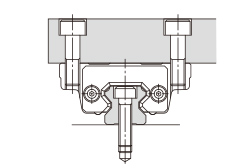
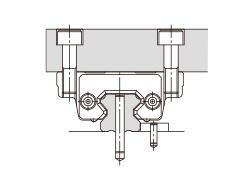
There are several ways of mounting the LM Guide as shown in Table1. When the machine is subject to vibrations that may cause the LM rail(s) or LM blocks to loosen, we recommend the securing method indicated by Fig.1. (If 2 or more rails are used in parallel, only the LM block on the master rail should be secured in the crosswise direction.) If this method is not applicable for a structural reason, hammer in knock pins to secure the LM block(s) as shown in Table2 When using knock pins, machine the top/bottom surfaces of the LM rail by 2 to 3 mm using a carbide end mill before drilling the holes since the surfaces are hardened.
| (a) Secured only with side reference surfaces | (b) Secured with set screws |
|---|---|
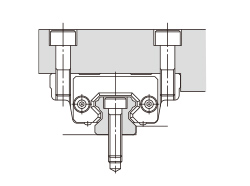 |
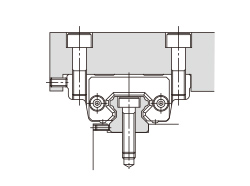 |
| (c) Secured with a presser plate | (d) Secured with tapered gibs |
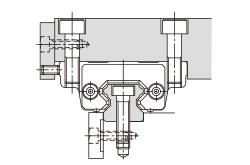 |
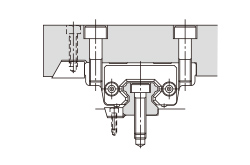 |
| (e) Secured with pins | |
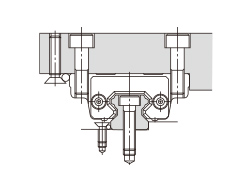 |
|
| (a) Secured only with the side reference surface of the rail | (b) Secured only with the side reference surface of the block |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| (c) Secured without a side reference surface | (d) Secured with dowel pins |
 |
 |