Calculating the permissible axial load
In Horizontal Mount
With ordinary conveyance systems, the axial load (Fan) applied when horizontally reciprocating the work is obtained in the equation below.
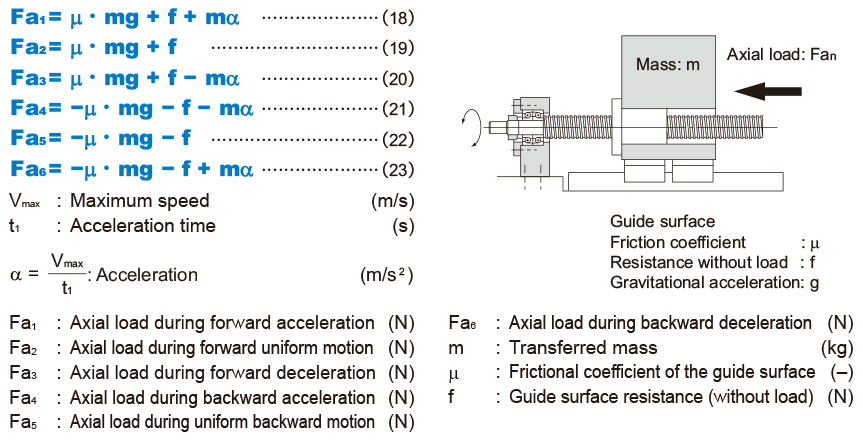
In Vertical Mount
With ordinary conveyance systems, the axial load (Fan) applied when vertically reciprocating the work is obtained in the equation below.
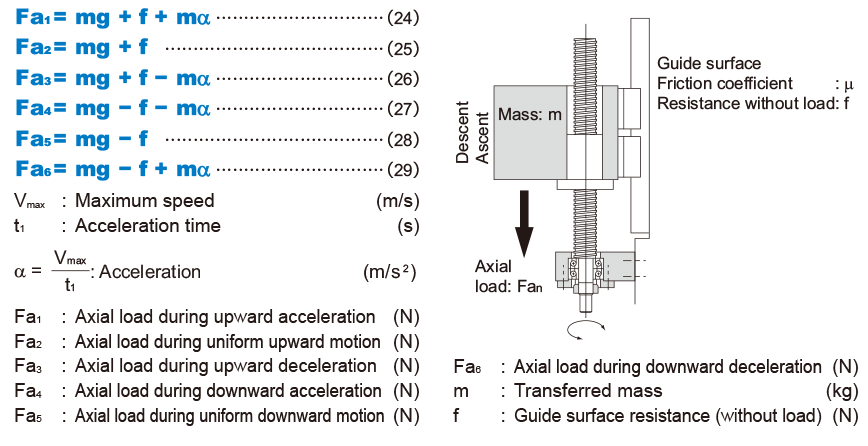
Static Safety Factor
Static Safety Factor per Basic Static Load Rating (Excluding Models HBN-V, HBN-K (KA), HBN, and SBKH)
For ball screws, a static safety factor as defined by Formula 30 based on the calculated maximum axial load and static load rating must be considered. Vibrations, impacts, or inertia due to starting and stopping may result in an unexpectedly large load. Therefore, please confirm that a sufficient static safety factor has been ensured when selecting a model. Estimates for the static safety factor are shown in Table 21.

| Load conditions3 | Lower limit of fs |
|---|---|
| Without vibration or impact | 2 |
| With vibration or impact | 5 |
Permissible Load Safety Margin (Models HBN-V, HBN-K (KA), HBN, and SBKH)
In comparison to previous ball screws, high-load ball screw models HBN-V, HBN-K (KA), HBN, and SBKH are designed to achieve longer service lives under high load conditions, and it is necessary to consider the permissible load Fp for the axial load. Permissible load Fp indicates the maximum axial load that the high-load ball screw can support, and this range should not be exceeded.
Permissible load Fp indicates the maxim axial load that the high load Ball Screw can receive, and this range should not be exceeded.

1 The basic static load rating (C0a) is a static load with a constant direction and magnitude whereby the sum of the permanent deformation of the rolling element and that of the raceway on the contact area under the maximum stress is 0.0001 times the rolling element diameter. With the ball screw, it is defi ned as the axial load. (Specifi c values of each ball screw model are indicated in the dimensional tables for the corresponding model number.)
2 The maximum axial load (Famax) applies to the maximum value of the axial load calculated in the calculation of the axial load.
3 In general, factors that cause vibration and impacts include acceleration and deceleration, sudden starts and stops, transmission of vibration and impacts from external devices and machines, and changes in processing force over time.
Point of Selection
- Conditions of the Ball Screw
- Conditions of the Ball Screw
- Estimating the shaft length
- Selecting lead・Selecting a shaft diameter
- Method for Mounting the Ball Screw Shaft
- Permissible Axial Load
- Permissible Rotational Speed
- Selecting a Nut
- Calculating the permissible axial load
- Considering the Service Life
- Studying the Rigidity
- Studying the Positioning Accuracy
- Studying the Rotational Torque
- Studying the Driving Motor