Static Safety Factor
During actual operation, damage may be caused by an unexpectedly large load acting on the LM Guide that is caused in particular by sudden starting and stopping, vibrations due to a cutting load, or a large moment created by an overhang. Therefore, a static safety factor (fs) must be considered. The static safety factor (fs) is obtained from the formulas in Table 9 based on the relationship between the applied load and the basic static load rating. Estimates for the static safety factor based on operating conditions are given in Table 10. In addition, the static safety factor (fs) must be considered for each direction (radial, reverse-radial, and horizontal) individually.
| When the radial load is large |  |
|---|---|
| When the reverse-radial load is large |  |
| When the lateral loads are large | 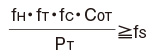 |
| Load conditions※2 | Lower limit of fS |
|---|---|
| Without vibrations or impacts | 2 |
| With vibrations or impacts | 5 |
- Note: For Model HRG, see the table below.
| Load conditions※2 | Lower limit of fS |
|---|---|
| Without vibrations or impacts | 4 |
| With vibrations or impacts | 4 |
| fS | Static safety factor |
|---|---|
| C0※1 | Basic static load rating (radial direction) (N) |
| C0L※1 | Basic static load rating (reverse-radial direction) (N) |
| C0T※1 | Basic static load rating (lateral direction) (N) |
| PR | Calculated load (radial direction) (N) |
| PL | Calculated load (reverse-radial direction) (N) |
| PT | Calculated load (lateral direction) (N) |
| fH | Hardness factor (Calculating the Nominal Life see Fig. 8) |
| fT | Temperature factor (Calculating the Nominal Life see Fig. 9) |
| fC | Contact factor (Calculating the Nominal Life see Fig. 10) |
- 1
The basic static load rating is a static load with a constant direction and size where the sum of the permanent deformation of the rolling element and that of the raceway on the contact area under the maximum stress is 0.0001 times the rolling element diameter.
- 2
In general, factors that cause vibration and impacts include acceleration and deceleration, sudden starts and stops, transmission of vibration and impacts from external devices and machines, and changes in processing force over time.